What is MSA? Measurement System Analysis
→ The full name is a Measurement System Analysis.→ A measurement system measures the quantification (data, number, or reading) of particular characteristics of any object. It also includes a combination of gages, fixtures, software, and personnel required to measure the characteristics of any object.
→ For better understanding, we are taking an example if we want to measure the weight of the product then the combination of operator, weighing scale, and our product is the whole measurement system.
→ Let us take another example if the weight of the product is automatically measured on a conveyer belt and recorded in software in this example measurement system includes the product, software, and conveyer.
→ MSA is a Statistical Tool that is used to determine if this system is capable or not?
Basics of Measurement System Analysis:
→ In our daily life, we are using more and more data for analysis so data has more value, and day by day it is increasing.→ This data is used for decision-making. If the collected data has an error due to measurement system error then there may be a chance of wrong decision making.
→ To avoid this problem MSA can help us to build a strong system for our data-based decision-making process.
→ We use various measuring instruments & gauges to judge the dimensional quality of Incoming, In-Process, and Finished Production parts.
→ These gauges and instruments have to be Precise and Accurate to give results of a higher confidence level.
→ To build this confidence, we have to calibrate these gauges/instruments periodically to achieve Accuracy and Precision.
➨ The sources of variation in a measuring process are due to the below factors:
⇢ Process
⇢ Personnel
⇢ Tools, Equipment, Gauges, Instrument, Fixtures, etc.
⇢ Product to be measured
⇢ Environmental (e.g. temperature, humidity, etc.)
➨ Below measuring instrument has a definite numerical scale to measure the numerical dimensions of the component.
→ E.g., Vernier, Micrometer, Dial indicator, Height Gauges…..
→ Vernier : Range: 0 – 200 mm L.C: 0.02mm; 0.01mm
→ Micrometer : Range: 0 -25; 25 – 50 L.C: 0.01mm; 0.001mm
→ "Resolution" is the ability to detect small changes.
→ "Sensitivity" is the smallest amount of difference in a quantity that will change an instrument's reading.
→ E.g. a measuring tape has a resolution, but not sensitivity, and an analytical balance have both resolution and sensitivity
➨ While selecting equipment, the following basic points need to be considered:
⇢ Range,
⇢ Least Count,
⇢ Accuracy and other relevant factors shall be considered.
➨ If we have a tolerance of 0.100 of a component, we should use the instrument with a Least Count of 0.010 mm. (which means the least count of the instrument should be 1/10th the tolerance range.)
Terminologies used in Measurement System Analysis:
→ There are certain terminologies that should be understood for better use of Gauges and Instruments which is mentioned below➨ Precision and Accuracy
➨ Repeatability and Reproducibility
→ It is extremely important in the Continuous Improvement of the process.
→ We must measure to know where we are.
→ For measurements to be effective, they must be timely, accurate, and precise.
→ Many of our customers, both internal and external, rely on our measurements.
→ We can get a Good Quality Product.
→ MSA deals with analyzing the effect of the Measurement system on the measured value.
→ Its emphasis on the effect due to equipment & personnel
→ We test the system to determine the numerical values of its statistical properties and compare them to Accepted Standards
→ Applicable to attribute data and variable data.
→ It reduces the likelihood of passing a bad part or rejecting a good part.
Why MSA is required?
→ It is required to understand the impact of these measurement systems on your operations.→ It is extremely important in the Continuous Improvement of the process.
→ We must measure to know where we are.
→ For measurements to be effective, they must be timely, accurate, and precise.
→ Many of our customers, both internal and external, rely on our measurements.
→ We can get a Good Quality Product.
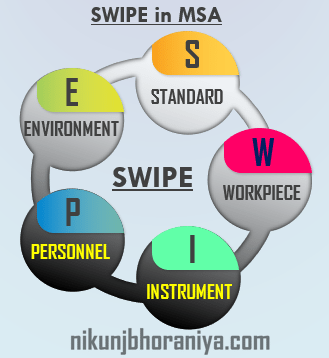
The Measurement System Analysis includes:
→ The SWIPE is included and the full name is mentioned below- Standard
- Work Piece
- Instrument
- Personnel / Procedure to use equipment
- Environment
→ MSA deals with analyzing the effect of the Measurement system on the measured value.
→ Its emphasis on the effect due to equipment & personnel
→ We test the system to determine the numerical values of its statistical properties and compare them to Accepted Standards
What is the purpose of an MSA?
→ The purpose of an MSA is to determine how much error is in the measurement due to the measuring process itself and quantifies the variability added by this system.→ Applicable to attribute data and variable data.
→ It reduces the likelihood of passing a bad part or rejecting a good part.
Types of MSA Study
- Variable GR&R Study
- Attribute GR&R Study
👉 See Also:





Requesting you to give information about attribute r and r
ReplyDeleteThank you for your valuable feedback we will update it.
DeleteDear sir
ReplyDeletePlease share the core tool ppt.
APQP,PPAP,MSA,SPC&FMEA.
Thank you.
All Presentations are available you can go to the sitemap and select the Quality Core Tools Thanks
DeleteThanks sir for your valuable information
ReplyDeleteYour way of training is very good and useful:)
Thanks for your kind words and feedback
DeleteHi please share Lean ,tpm and LSS masterplans or roadmaps implementation examples
ReplyDeleteThank you for your feedback we will definitely work on that.
DeleteThanks for explaining every topic so well.
ReplyDeleteThanks and Happy Learning!!!
DeleteNice Core Tool & IATF Information .Could please give information VDA
ReplyDeleteSure we will share it soon.
DeleteIN VDA - Core Tool ,Process Audit , DT/LTD
ReplyDeleteHi thanks for the suggestion.
DeleteIf the appraisers are more than 10 and also samples are more than 5. Then how to use MSA excel sheet. Kindly share sheet with n numbers of Appraisers and samples.
ReplyDeleteYou can reach us at: contact@nikunjbhoraniya.com
DeletePost a Comment