What is Lean Six Sigma?
→ Lean Six Sigma is a fact-based, data-driven philosophy of improvement methodology that is focused on defect prevention rather than defect detection.→ It is a combination of two different powerful process improvement methodologies, (1) Toyota's Lean_Manufacturing philosophy and, (2) Motorola's Six Sigma management strategy.
→ It is a data-driven approach to increase profit, and the satisfaction of the customer, and improve effectiveness and efficiency.
→ This is a team-focused managerial approach that seeks to improve performance by eliminating waste and variations.
Lean Six Sigma Principles
- Primary focus on the consumer.
- First time through
- Improve the Value Stream
- Eliminate the Non-value added processes
- Decision-based on facts and data
- Engage the people
- A systematic approach for continuous improvement
Lean Concept:
→ "Lean" refers to any method or tool that helps to identify and eliminate waste. This concept focuses on the elimination of the 8 kinds of waste known as "TIMWOODS" or "DOWNTIME".→ TIMWOODS is an abbreviation of wastes such as Transportation, Inventory, Motion, Waiting, Over Production, Over Processing, Defect, Skill-set, or non-utilized talent.
→ Lean is introduced by Toyota and Taiichi Ohno. It has its origin as the Toyota Production System (TPS). It is very much about improving operation flow, reducing waste, and maximizing profit.
→ This concept has evolved over the years into a system for both manufacturing and service sectors.
→ By improving this we can get more productivity.
Six Sigma Concept:
→ Six_Sigma improves manufacturing processes by using tools and techniques.→ In the 1980's, Motorola with his team of engineers developed this concept. It helped Motorola to improve its profit and product quality.
→ Its intent is to improve processes by identifying and eliminating the causes of defects and variations in business and manufacturing processes.
→ In this tool the DMAIC is a very important framework that stands for Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, and Control.
→ It is a decision-making method based on data and statistics for improving, optimizing, and stabilizing business and manufacturing processes.
→ This was not only a standard to measure productivity, but also it measures a cultural change in the organization.
→ After the success in Motorola, this technique has been adopted by many companies in the world.
How Lean Six Sigma concept was born?
→ By combining two different methodologies, Lean_Six_Sigma was born and then it becomes an effective system that improves product quality and minimizes wastes in a system or process.→ It helps all businesses to improve their performances.
→ A combined management approach, LSS amplifies the strengths and minimizes the weaknesses of both approaches when used alone.
→ The first concept of this method was introduced in Barbara Wheat's book in 2001. (source: Wikipedia)
→ Then it follows the use of Six_Sigma methodologies and tools to identify and reduce variation in a system or process.
→ Most of the organizations now choose to use this tool.
Lean Six Sigma Belts
- Yellow Belt: This is referred to as basic awareness
- Green Belt: A focus on the use of tools and the application of DMAIC and lean_principles
- Black Belt: Full-time project leader
- Master Black Belt: A Black Belt with a minimum of two years of experience. Able to guide the Black Belt.
→ Based on belts holding the Six_Sigma Project team member and their roles and responsibilities defined.
Lean Six Sigma Methodology
- DMADV - used to design new products, services, and processes
- DMAIC - used for improvement activity in current running products, services, and processes.
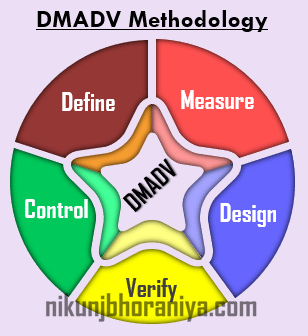
What is DMADV in Lean Six Sigma?:
→ This methodology is used to design new products, services, and processes.
➨ Define:
⇢ In this phase, everyone who participated in the project knows their role.
⇢ Discuss with the team, why you are doing the project, and what you are trying to achieve with the project.
➨ Measure:
⇢ In this phase, you need to focus on defining and understanding customer needs.
⇢ We have to create a complete picture of the current process state and establish current baselines.
⇢ Also, check your process capability in this phase.
➨ Analyze:
⇢ Now you can move from what the customer needs to how you might achieve this.
⇢ Identify key functions and characteristics.
⇢ Analyze the functions to check their capability and ensure that they are fit for purpose.
➨ Design:
⇢ At this stage, you need to add detail to the various elements of the design.
⇢ Check the performance of the design on the prototype sample and evaluate the capability of the design.
➨ Verify:
⇢ This is where you want to assess the achievements made and the lessons learned.
⇢ Verify the results in relation to the original specifications and targets.
What is DMAIC in Lean Six Sigma?:
→ This methodology is used for improvement activity for an already ongoing process, product or service.
➨ Define:
⇢ Projects start with a problem that needs solving.
⇢ In this phase, everyone who participated in the project knows their role.
⇢ Discuss with the team, why you are doing the project, and what you are trying to achieve with the project.
➨ Measure:
⇢ As per the problem defined in the Define phase, some work done based on that.
⇢ During the Measure phase, you need to clarify things by seeing how the work gets done.
➨ Analyze:
⇢ In the Analyze phase, you know what is happening?
⇢ It is time to find out why this is happening?
⇢ Based on the fact to check out the possible causes and get to the root cause.
➨ Improve:
⇢ In the Improve_phase, we need to know about the process and the problem.
⇢ And we need to find out the best solution to the root cause.
⇢ In the Improve_phase, the team checks the sustainability of the changes were made during the project.
➨ Control:
⇢ The control phase is the final phase of the DMAIC Methodology.
⇢ In the control phase, Update Documentation like Standard operating procedures (SOP's), Control plan, Process Maps, Work Instructions, Visual Aids, etc.
⇢ So that we can ensure that the process is carried out consistently.
Benefits of Lean_Six_Sigma:
→ It helps the organization to grow business in the following ways: Increases Profit, Decreases Manufacturing Costs, Improves Efficiency & Effectiveness→ Helps to Develop People/Employee friendly working culture
→ Customer Satisfaction
→ Improve Product Quality
→ Reduce wasteful activity and improve productivity
→ Creates a competitive advantage for the organization
→ It helps to improve the efficiency and quality of the process.
👉 See Also:





This is a good overall primer to Lean Six Sigma - great job!
ReplyDeleteThank you
DeleteGood scalable knowledge in single PPT
ReplyDeleteThanks and Happy Learning.
DeleteI can't to join what's app link?
ReplyDeleteKindly share details us at: contact@nikunjbhoraniya.com
DeletePost a Comment