What is Why Why ANALYSIS?
→ "Why-Why" analysis is an analytical method that is designed to help you identify all factors contributing to a problem one by one in an orderly fashion, rather than a hit-and-miss attempt to work out the factors and finally, we will have the root cause for the failure.→ Sakichi Toyoda developed this technique and firstly used it within the Toyota Motors.
→ It is a critical component of problem_solving training and also the same was delivered as part of the induction training into the Toyota Production System for the newly joined employees.
→ This method is also used during the implementing of Kaizen, Lean Manufacturing, and Six Sigma projects.
→ Before going further we will discuss some fundamental concepts which are very important for understanding the 5 why method.
→ 90% of problems can be solved only by why-why analysis.
→ The remaining 10% of problems need a high level and complex methodology for solving.
→ Understand the issue – observe the issue closely, at the spot, on the actual thing, and collect all related information.
→ Problem observation will lead to a conclusion
→ The conclusion may lead to the root cause or will lead to the starting of the 5 Why method.
→ This method is a very famous Root Cause Analysis Method.
Why problem analysis is required?
→ The problem analysis is required to prevent the recurrence of the failure.
→ To find out the root cause and we can easily take preventive action against that.
→ It is also very helpful for developing our problem-solving skills and mitigating future challenges.
You can refer to this article for a better understanding of Various Problem Solving Methods
You can refer to this article for a better understanding of Various Problem Solving Methods
What is the problem, cause, root cause, and countermeasure?
→ The problem is what has happened. or it is an undesirable event.
→ Issue Observation is an understanding of what has happened.
→ The cause is the reason behind the failure.
→ The root cause is exactly where the cause has originated.
→ Counter-measure: The action which you take against the root cause so the issue will not be repeated again.
Key Points of Why-why Analysis
→ It should be done in a team→ Verify facts from Genba – the real place, and on Genbutsu – the real thing.
→ Connect the why-s in a chain of logic
→ Should end up the investigation where the causes can be prevented
→ Use the ‘hence’ logic to check the chain of logic is continuous
→ No assumptions, No guesses
→ Keep management in the loop during the five whys process in the company.
→ Use paper or whiteboard instead of computers because that is a more effective method.
→ Write down the issue and make sure that all people understand it.
→ Distinguish causes and symptoms. Don't mix up causes and symptoms.
→ Keep the focus on the logic of the cause_and_effect relationship.
→ Try to make your answers more precise.
→ Look for the cause step by step. Don't jump to conclusions.
→ Assess the process, not the people.
→ Never consider root cause as "human error" or "worker's inattention".
→ Ask "why" till the root cause is determined.
How to perform a Why-why analysis?
→ Repeat ‘why’ n-times (till root cause is found)→ Applicable for one single event
→ Stop the why chain when you reach the basic 5-causes
→ Can be done by Gemba people based on actual findings
→ It is not mandatory to stop after asking 5 why's sometimes we can reach at the root cause by less than 5 whys and sometimes it can go up to more than 5 whys.
Idea of countermeasure
→ Countermeasure is just opposite of the root_cause identified→ Example:
⇢ Final Why - No FG part checking standards are available in place
⇢ Counter Measure - Establish and display the FG part checking standard at the FG part checking area.
Example of 5 why analysis:
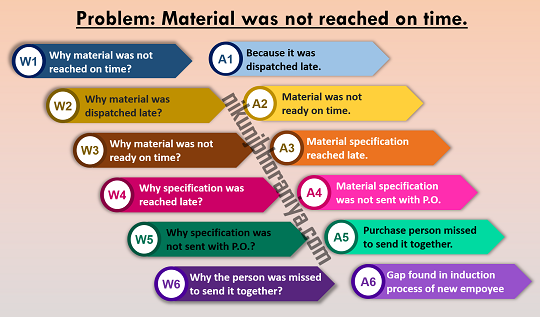
➨ Problem: Material was not reached at the site on time.→ Why-01: Why material was not reached on time?
⇢ Ans-01: Because it was dispatched late.
→ Why-02: Why material was dispatched late?
⇢ Ans-02: Material was not ready on time.
→ Why-03: Why material was not ready on time?
⇢ Ans-03: Material specification reached late.
→ Why-04: Why specification was reached late?
⇢ Ans-04: Material specification was not sent with P.O.
→ Why-05: Why specification was not sent with P.O.?
⇢ Ans-05: Purchase person missed to send it together.
→ Why-06: Why the person was missed to send it together?
⇢ Ans-06: The gap found in the induction process of a new employees.
➨ Root_Cause: The gap found in the induction process of new employees. [Process/System Failure]
➨ Preventive_Action: Introduce a training system for new joiners is updated.
Benefits of 5 Why Analysis:
→ Improving analytical thinking.→ Develop an understanding of the relation of the failure with theories & fundamental principles.
→ Improve the knowledge of the function, structure, and mechanism of the equipment/process.
→ Develop the consciousness about the abnormalities causing troubles in the workplace.
→ Aim to level up the ability of the people.
→ Develop the way of prevention of recurrence.
👉 See Also:




Nice
ردحذفThank you!!!
حذفvery usefull for me,let me use this knowlegde in my company.Thank you very much.
ردحذفHappy to hear that from you.
حذفThanks and happy learning.
this website is best website I had visited
ردحذفThank you very much for your kind comment and happy learning!!!
حذفIt's really useful to all segments of industries.. Great work... Keep it up..
ردحذفThanks and Happy Learning!!!
حذفGreat effort and very good source to start
ردحذفThank you so much for your kind comment!!!
حذفIt's wonderful
ردحذفRespect
ردحذفThanks and Welcome
حذفThis is really helpful
ردحذفThanks and Happy Learning
حذفإرسال تعليق